
compact heat exchangersĬontains a large number of tubes packed in a shell with their axes parallels to that of the shell. The presence of mixing can have adverse and significant effects on the heat transfer characteristics of a heat exchanger.
#TEMA EXCHANGER TYPES FREE#
The fluid is free to move in the transverse direction. Plate fins force the fluid to flow through a particular inter-fin spacing and prevent it from moving in the transverse direction. This type of flow may be classified as unmixed or mixed. The two fluids in this type of heat exchangers move in directions perpendicular to each other, a flow configuration referred to as cross-flow. They are mostly used in gas-to-gas and gas-to-liquid heat exchanger to counteract the low heat transfer coefficient associated with fluid flow with increased surface area. They are therefore best suited for applications with strict limitations on the weight and volume of heat exchanger. They allow high heat transfer rates between fluids in a small volume. car radiator, human lung am0ongest others. Heat exchangers with β >700 are classified as compact heat exchanger e.g. The ratio of the heat transfer surface area of a heat exchanger to its volume is called the area density β. Shell and tube heat exchangers come in a variety of styles and materials to help each customer achieve their heat transfer goals.This type of heat exchanger is designed to allow a large heat transfer surface area per unit volume. This material is available exclusively through Ametek Fluoropolymer Products. Fluoropolymer (FEP, PFA, and “Q” resins) “Q” is a special fluorocarbon compound that significantly improves thermal efficiency and increases temperature and pressure capabilities.Examples of the more common materials of construction are listed below: This is dependent upon the fluids, pressures, and temperatures used within the heat exchanger. Baffles – Baffles are plates that direct shell fluid flow around the tube bundle to promote heat transfer.Įvery process need will be different and thus have a different need for their heat exchanger materials of construction.Tube Sheet – The tube sheet is used to support and isolate the tubes within a shell and tube heat exchanger.Tube bundle –The bundle is inserted into the pressure vessel and process fluid is run through for heating or cooling purposes.Shell, or pressure vessel – is where a cooling or heating fluid will flow through to transfer heat or remove heat from a tube bundle.
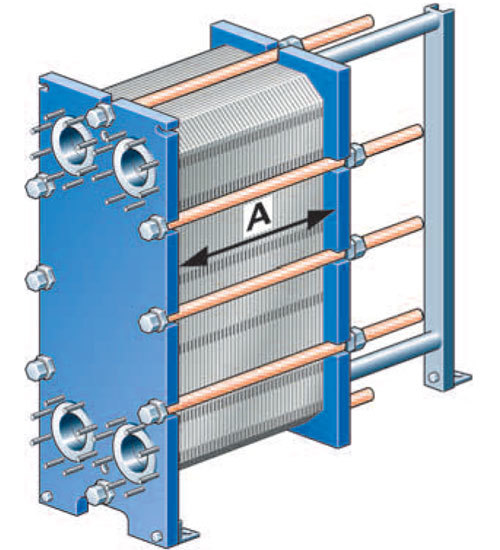
The standard construction of a shell and tube heat exchanger consists of the following: Though the standard construction of a shell and tube heat exchanger is simple in design there are different varieties, materials, and configurations to suit a multitude of industry needs. These heat exchangers have long been the choice by industrial and commercial personnel and with high popularity among these individuals comes a variety of shell and tube heat exchanger types. Shell and tube heat exchangers are one of the most popular types of heat exchanger because of their flexibility to accommodate a wide range of temperatures and pressures.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
